Email cannot be empty
Password cannot be empty
Email format error
Email cannot be empty
Email already exists
6-20 characters(letters plus numbers only)
The password is inconsistent
Email format error
Email cannot be empty
Email does not exist
6-20 characters(letters plus numbers only)
The password is inconsistent

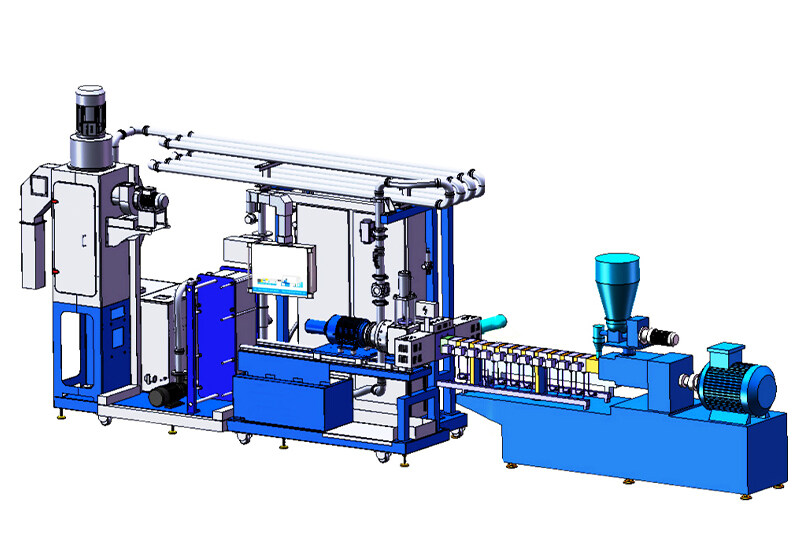
Many manufacturers are choosing die-face pelletizing for several reasons:
01 Process and Principle of Die-face Pelletizing
As shown in the figure below, the pelletizing system mainly includes the following equipment: a reversing valve, a cutting chamber, a die plate, a pelletizer with a driving system, cooling pipelines, and drying machines with water systems, vibrating sieves, etc. With the continuous improvement of single-line capacity, the maximum capacity of pelletizers currently used in SAN and ABS pellet production can reach over 10,000 kg/h.
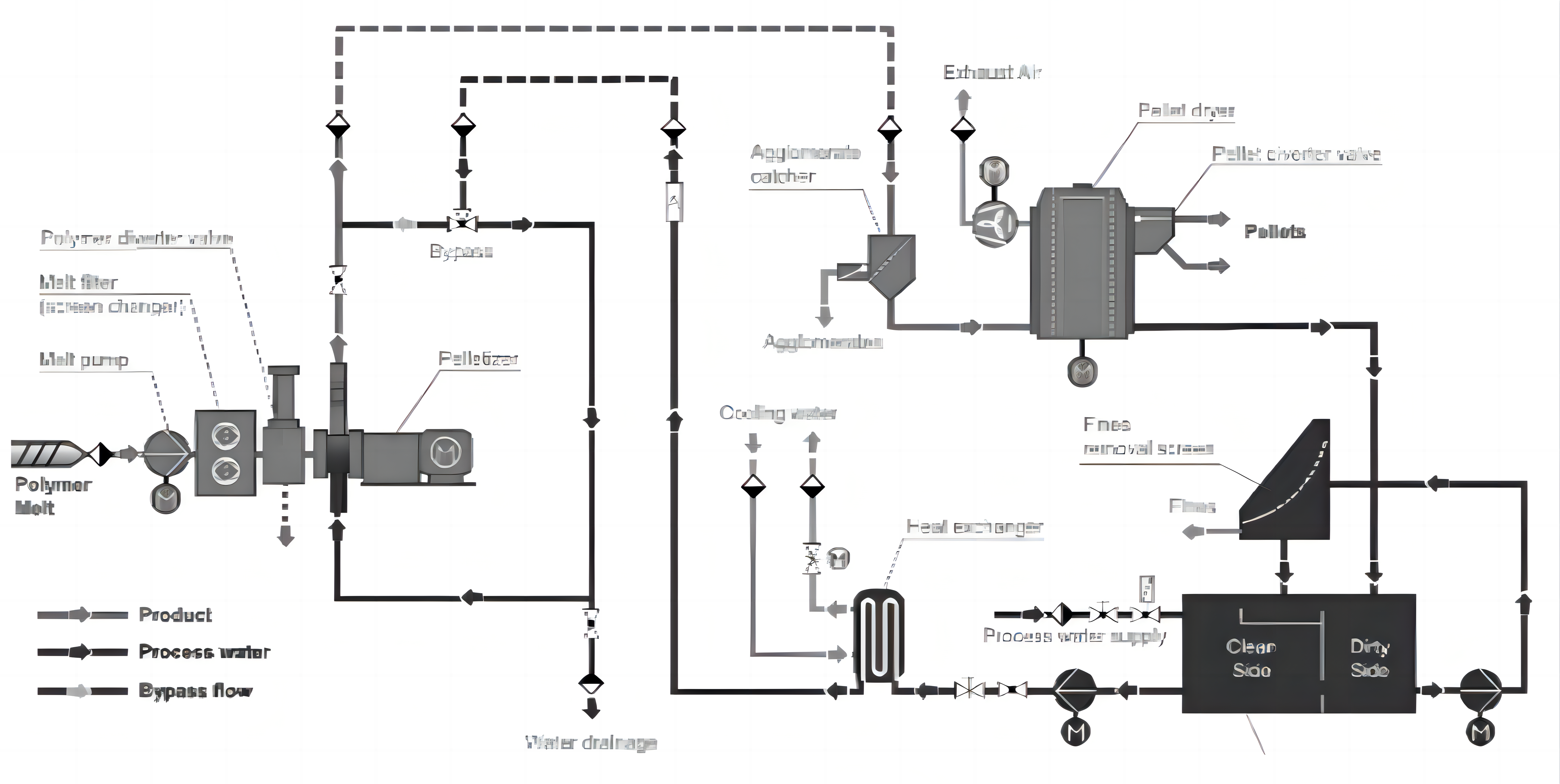
The main working principle of the die-face pelletizing system is as follows: The material is conveyed to the drive valve and cutting chamber through a bottom pump or gear pump. The material is cut by the driven cutter of the pelletizer in a molten state. The pellets are then cooled in circulation, with the water temperature generally ranging from 40 to 60°C. The pellets are sent to a centrifugal dehydrator for drying. The process water circulates back to the water system for filtration, heat exchange, and then returns to the process system for reuse.
02 The construction of die-face pelletizing:
The production of die-face pelletizing results in round or oval-shaped pellets. The process involves high-temperature cutting, where the surface of the pellets quickly cools while the internal heat is used for self-drying, requiring lower process water temperatures. The pelletizer itself has a small footprint and utilizes vertical space for cooling pipeline layout, reducing the overall footprint to 3-6m (depending on the model). The equipment can be installed on different floors, avoiding linear layout and saving space.
Pellets are cut in a molten state, quickly cooled on the surface, and then transported in cooling pipelines and centrifugal dehydrators. The pellets have point-to-point contact, reducing the likelihood of dust generation during transport in the pipelines and centrifugal dehydrators. The dust content is reduced by approximately 10%-15%, and the pellets are cut in a hot state with low dust generation.
The die-face pelletizing system is a closed system, eliminating the need for separate dust collection equipment, making it environmentally friendly. It also does not require additional auxiliary exhaust gas treatment equipment, which is an important improvement in equipment investment and environmental protection. The die plate replacement time is 15-30 minutes, and the blade replacement time is around 5 minutes.
03 Die-face pelletizing offers several operational advantages:
Efficiency:
It is a continuous process that allows for high production rates with minimal downtime.
Quality:
Die-face pelletizing produces uniform pellets with consistent size and shape, ensuring high-quality end products.
Energy Efficiency:
The process requires less energy compared to other pelletizing methods, leading to lower operating costs.
Space Savings:
Die-face pelletizing equipment has a compact design, saving floor space in manufacturing facilities.
Environmental Friendliness:
It is a closed-loop system that minimizes waste and dust generation, making it environmentally friendly.
Ease of Operation:
Die-face pelletizing is relatively easy to operate and requires minimal maintenance, reducing labor costs and downtime.
04 Die-face pelletizing offers several product advantages:
In the production process of water-cooled strand pelletizing, the strip-shaped material cut by the moving cutter already has a certain hardness and is prone to generating dust. In contrast, die-face pelletizing involves cutting the melt at the die head by the blades, resulting in much less dust during cutting compared to underwater strand pelletizing. The higher bulk density of round pellets results in smaller contact area between particles, leading to less dust generation. Additionally, round pellets have a smaller volume for the same mass, smooth surfaces, and are easier to transport.
Circular particles, unlike the cylindrical particles produced by water-cooled strand pelletizing, lack edges and corners, making them less likely to generate dust when they rub against each other. On the other hand, cylindrical particles produced by underwater strand pelletizing are more prone to dust generation. Additionally, the spherical surface of circular particles allows for a more uniform melting speed in downstream processes, requiring less energy. The specific comparison is shown in Table 1.
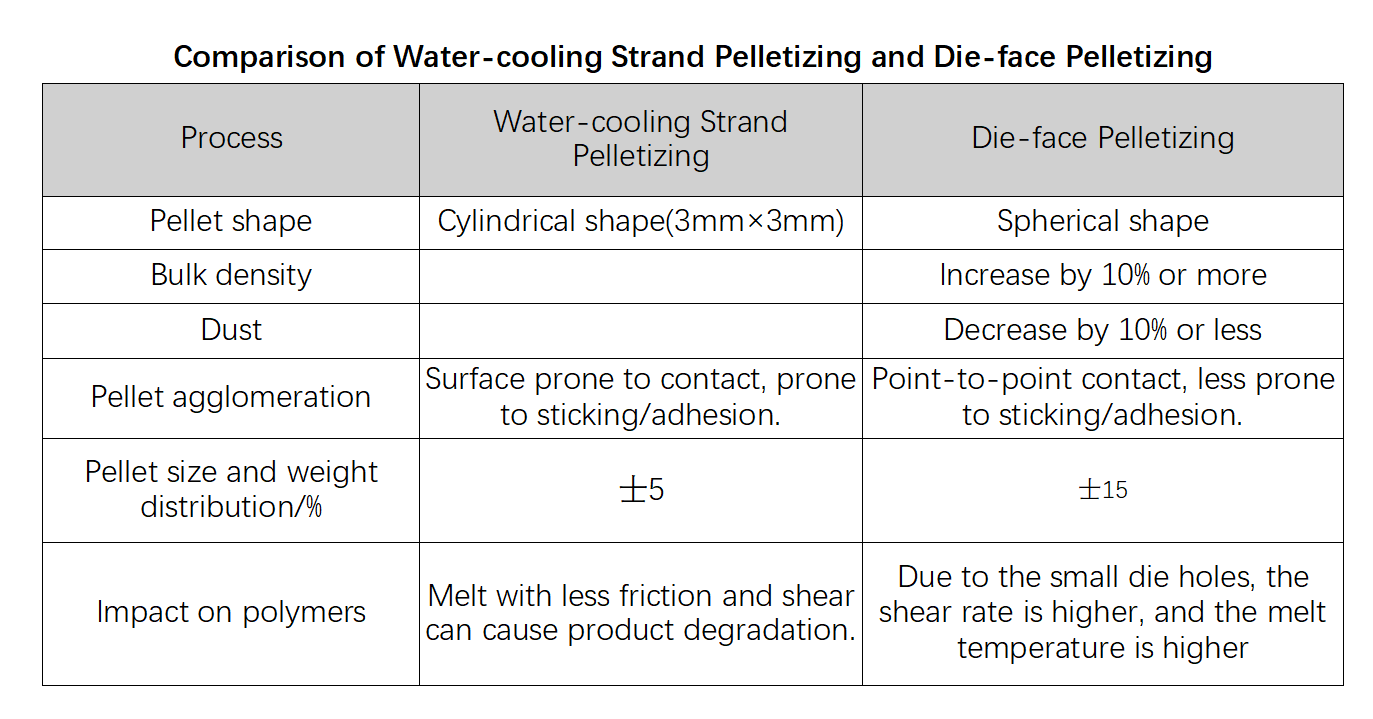
05 Die-face pelletizing offers several cost advantages:
Reduced Maintenance Costs: The equipment used in die-face pelletizing tends to have simpler designs and fewer moving parts, leading to lower maintenance costs over time.
Energy Efficiency: Die-face pelletizing requires less energy compared to other methods, resulting in lower operating costs.
Less Waste: Die-face pelletizing produces less waste material compared to other methods, reducing disposal costs.
Space Savings: Die-face pelletizing equipment has a compact design, saving floor space in manufacturing facilities.
Higher Productivity: Die-face pelletizing is a continuous process that can achieve high production rates, leading to higher productivity and potentially lower unit costs.
The blade cost of die-face pelletizing is very low because the blade material is ordinary and does not require high hardness.
06 Application of Die-face pelletizing
Die-face pelletizing is widely used in the production of SAN resin, mainly due to the process's specificity and the characteristics of SAN resin itself. The main issue in the production process is the presence of a significant amount of powder in the SAN resin. Additionally, there is a need to improve the selection criteria for the water tank. If the selection criteria are too low, the material is not thick enough, the hardness is insufficient, and the water tank is operated for a long time, the drum in the water tank is prone to deformation, the rollers wear out more quickly, and the service life is reduced. The motor driving the drum rotation can also be damaged, causing the equipment to malfunction and requiring maintenance, which can lead to production load adjustments and many troubles in production. Fluctuations in production can also affect product quality, leading to a large number of non-conforming products and increasing production costs.
For ABS resin, which has greater toughness, the selection of cutting tools differs from that for SAN resin. Typically, angled cutters are used, and the specific material is determined based on the grade of the resin. The requirements for the extruder are an inlet pressure of 80-120 bar for the die head, 180-220 bar for the screen changer, and positive pressure for the booster pump. Generally, co-rotating twin-screw extruders can meet these requirements.